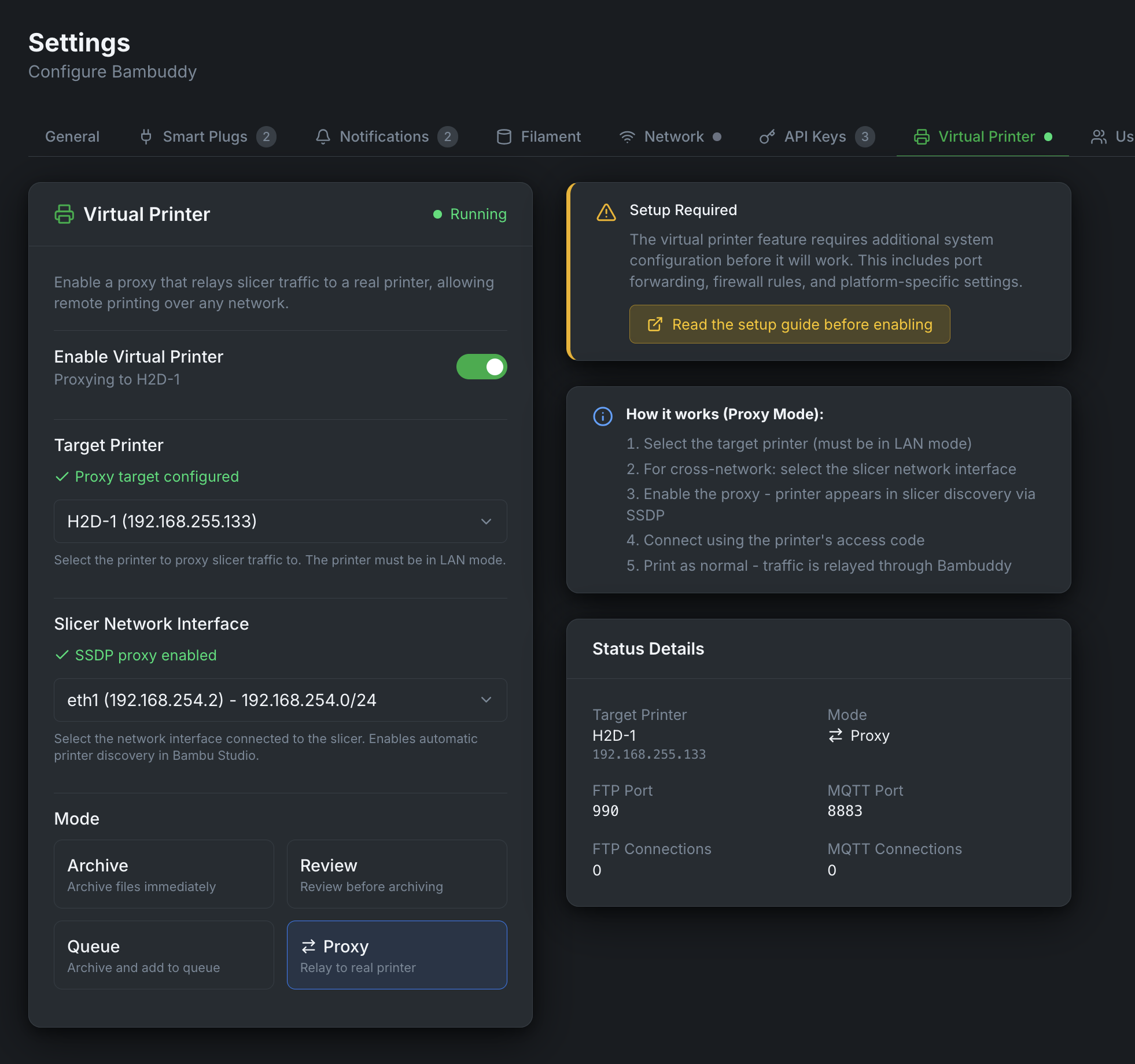
Virtual Printer¶
The Virtual Printer feature allows Bambuddy to emulate a Bambu Lab printer on your network. This enables you to send prints directly from Bambu Studio or Orca Slicer to Bambuddy, even without a physical printer connected.
Overview¶
When enabled, Bambuddy creates a virtual printer that:
- Appears automatically in Bambu Studio/Orca Slicer via SSDP discovery
- Accepts print jobs over secure TLS/MQTT connections
- Archives prints directly or queues them for review
- Works with the same workflow as sending to a real Bambu Lab printer
Use Cases¶
- Print Archiving: Send prints to Bambuddy for archiving without starting them
- Queue Building: Build up a print queue before your printer is available
- Print Farm Preparation: Prepare jobs to distribute across multiple printers
- Remote Slicing: Slice on one computer and send to Bambuddy running elsewhere
- 🌐 Remote Printing: Print from anywhere via Proxy Mode (see below)
Proxy Mode - Remote Printing¶
NEW FEATURE
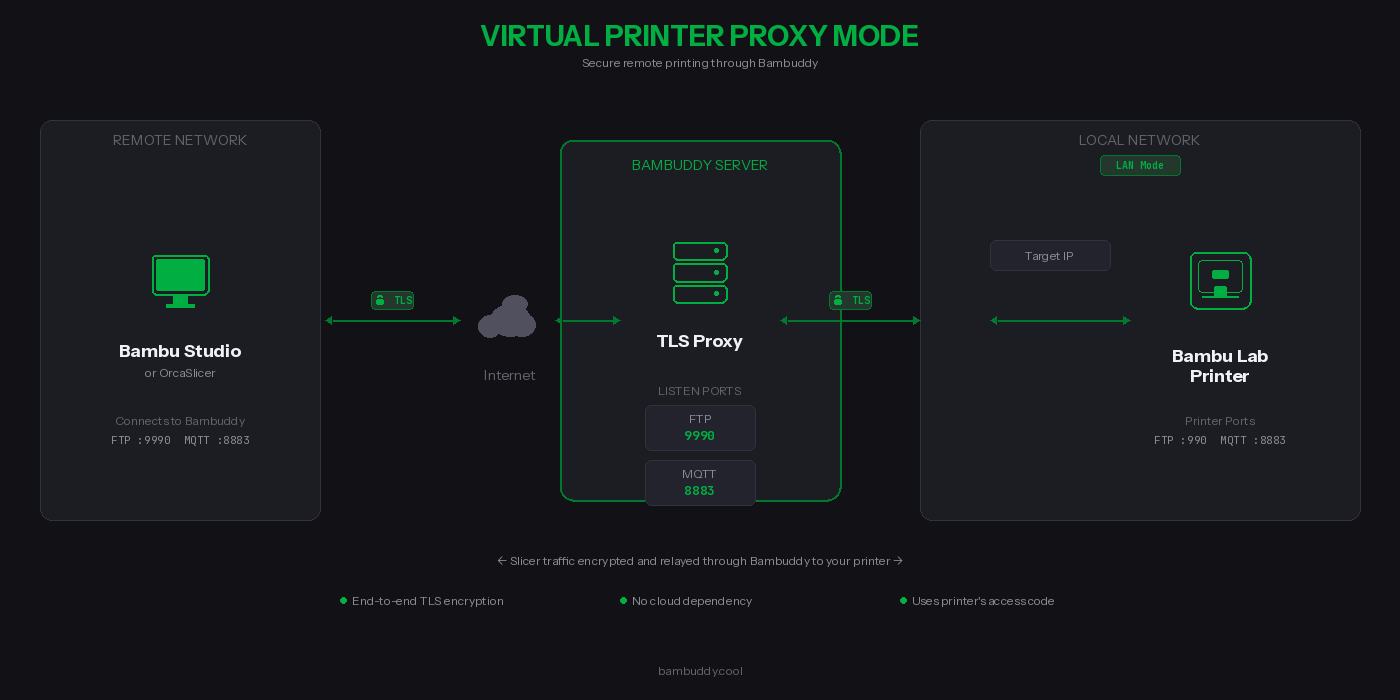
Proxy Mode enables remote printing from anywhere in the world through a secure TLS relay.
What is Proxy Mode?¶
Unlike the standard virtual printer modes that archive files locally, Proxy Mode forwards your print jobs directly to a real Bambu Lab printer. Bambuddy acts as a secure relay between your slicer and your printer.
How It Works¶
- Select the target printer (must be in LAN mode)
- For cross-network: select the slicer network interface for SSDP relay
- Enable the proxy - printer appears in slicer discovery via SSDP
- Connect using the printer's access code
- Print as normal - traffic is relayed through Bambuddy
- Camera streaming requires NAT/IP forwarding (see below)
Key Benefits¶
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
 TLS-encrypted control channels TLS-encrypted control channels | MQTT and FTP control fully encrypted; use VPN for data channel |
 No cloud dependency No cloud dependency | Your data never touches third-party servers |
 Uses printer's credentials Uses printer's credentials | No additional passwords - use your printer's access code |
 Full protocol support Full protocol support | Both FTP (file transfer) and MQTT (control) are proxied |
 Connection monitoring Connection monitoring | Real-time status showing active connections |
FTP Data Channel Security
Bambu Studio's FTP implementation does not encrypt the data channel — even though it negotiates PROT P (encrypted), it sends file data in cleartext. The MQTT control channel (commands, status) is fully TLS-encrypted.
What this means: Your 3MF print files are transferred unencrypted between the slicer and Bambuddy. Between Bambuddy and your printer, the data channel is encrypted.
Recommendation: When using Proxy Mode over the internet, place a VPN (WireGuard, Tailscale, or similar) between your slicer and Bambuddy to protect the FTP data channel.
Proxy Mode Ports¶
| Protocol | Bambuddy Listen Port | Printer Port | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| FTP/FTPS | 990 | 990 | File transfer control (TLS) |
| FTP Data | 50000-50100 | 50000-50100 | File transfer data |
| MQTT/TLS | 8883 | 8883 | Printer control & status (TLS) |
Privileged Port
Port 990 is a privileged port. For bare metal installs using systemd, add AmbientCapabilities=CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE to your service file. For Docker with host networking, no additional configuration is needed.
Requirements¶
Printer Requirements:
- Bambu Lab printer in LAN Mode (Developer Mode)
- Printer must be accessible from Bambuddy on your local network
- Printer's IP address and access code
Network Requirements:
- Bambuddy server accessible from the internet (or your remote network)
- Ports 990 (FTP control), 8883 (MQTT), and 50000-50100 (FTP data) reachable from the remote slicer
- Static IP or dynamic DNS for your Bambuddy server
Supported Network Configurations:
| Setup | SSDP Discovery | Manual Add | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Same LAN | Automatic | Yes | SSDP broadcast reaches slicer directly |
| Dual-homed (2 NICs) | Automatic | Yes | Use Network Interface Override to select correct NIC |
| Docker host mode (Linux) | Automatic | Yes | Host networking passes SSDP traffic |
| Docker bridge mode | Not available | Required | Bridge networking blocks UDP multicast |
| VPN (WireGuard/Tailscale) | Not available | Required | VPN tunnels don't carry UDP multicast |
| Port forwarding / internet | Not available | Required | SSDP is local-network only |
Network Interface Override (All Modes):
Multi-NIC / Docker / VPN Users
If Bambuddy has multiple network interfaces (e.g., LAN + Tailscale, Docker with multiple bridges), the auto-detected IP may be wrong. Use Network Interface Override in Virtual Printer settings to select the correct interface.
This applies to all modes (Archive, Review, Queue, and Proxy) and affects:
- The IP address advertised via SSDP discovery
- The IP included in the TLS certificate (SAN)
Dual-Homed (Cross-Network) Setup:
For setups where Bambuddy has interfaces on two networks (e.g., printer on LAN A, slicer on LAN B):
- Enable the virtual printer, then select the correct interface under Network Interface Override
- In Proxy mode, Bambuddy will re-broadcast printer SSDP on the slicer's network
- In other modes, SSDP broadcasts and TLS certificates use the selected interface IP
- The slicer discovers the printer automatically via SSDP
- Camera streaming requires additional NAT/iptables rules (RTSP port 322)
Single Interface + Port Forwarding Setup:
For remote access where Bambuddy and printer are on the same network:
- Configure port forwarding on your router (ports 990, 8883, 50000-50100 to Bambuddy)
- Remote user manually adds printer in slicer using Bambuddy's public IP/hostname
- No automatic SSDP discovery (slicer is on a different network)
Setting Up Proxy Mode¶
Step 1: Configure Ports for Your Installation¶
Choose your installation type below:
No additional port configuration needed!
Host mode exposes all ports directly. Just ensure your firewall allows the ports:
# UFW
sudo ufw allow 990/tcp comment "Bambuddy Proxy FTP"
sudo ufw allow 8883/tcp comment "Bambuddy Proxy MQTT"
sudo ufw allow 50000:50100/tcp comment "Bambuddy Proxy FTP Data"
# Or firewalld
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=990/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=8883/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=50000-50100/tcp
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Add port mappings to your docker-compose.yml:
services:
bambuddy:
image: ghcr.io/maziggy/bambuddy:latest
container_name: bambuddy
ports:
- "${PORT:-8000}:8000" # Web UI
- "990:990" # Proxy FTP control
- "8883:8883" # Proxy MQTT
- "50000-50100:50000-50100" # Proxy FTP passive data
volumes:
- bambuddy_data:/app/data
- bambuddy_logs:/app/logs
environment:
- TZ=Europe/Berlin
restart: unless-stopped
volumes:
bambuddy_data:
bambuddy_logs:
Then restart the container:
No SSDP Discovery
Bridge mode doesn't support SSDP discovery. You must add the printer manually in your slicer using the IP address.
For systemd-managed services, add capability for privileged port binding:
Then open ports in your firewall:
# UFW (Ubuntu/Debian)
sudo ufw allow 990/tcp comment "Bambuddy Proxy FTP"
sudo ufw allow 8883/tcp comment "Bambuddy Proxy MQTT"
# Or iptables
sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 990 -j ACCEPT
sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 8883 -j ACCEPT
sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 50000:50100 -j ACCEPT
# Make iptables rules persistent (Debian/Ubuntu)
sudo apt install iptables-persistent
sudo netfilter-persistent save
If using host network mode, open firewall ports as shown in the Linux Native tab.
If using bridge mode, add port mappings in the container configuration:
990:990(TCP) - Proxy FTP control8883:8883(TCP) - Proxy MQTT50000-50100:50000-50100(TCP) - Proxy FTP passive data
Step 2: Configure Remote Access (Router Port Forwarding)¶
To access from outside your home network, forward these ports on your router:
| External Port | Internal Port | Protocol | Destination |
|---|---|---|---|
| 990 | 990 | TCP | Bambuddy server IP |
| 8883 | 8883 | TCP | Bambuddy server IP |
| 50000-50100 | 50000-50100 | TCP | Bambuddy server IP |
Recommended: Use a VPN
For best security, use a VPN like Tailscale or WireGuard between your slicer and Bambuddy. This encrypts all traffic including the FTP data channel (see security note above).
Other options:
- Cloudflare Tunnel — Free tunneling (TCP passthrough for ports 990, 8883, 50000-50100)
- nginx/Caddy/Traefik — Reverse proxy for web UI only; FTP/MQTT need direct access
Security Note
These ports will be exposed to the internet. The MQTT and FTP control channels are protected by TLS encryption and your printer's access code. The FTP data channel is not encrypted on the slicer side — use a VPN for full encryption.
Step 3: Enable Proxy Mode in Bambuddy¶
- Go to Settings → Virtual Printer
- Select Proxy mode from the mode options
- Select your Target Printer from the dropdown
- Click the toggle to Enable Virtual Printer
- Verify the status shows "Running" with the proxy ports
Step 5: Configure Your Slicer¶
In Bambu Studio or OrcaSlicer:
- Go to Device → Add Printer → Add printer manually
- Enter your Bambuddy server's external IP or hostname
- Enter your printer's access code (not a Bambuddy password)
- The printer should connect and show as online
Step 6: Print!¶
Select a model, slice it, and click Print. The job will be:
- Sent to Bambuddy over the internet (encrypted)
- Relayed to your printer on the local network (encrypted)
- Started on your printer just like a local print
Proxy Mode Use Cases¶
| Use Case | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote Print Farm | Manage workshop printers from home or office |
| Traveling Makers | Start prints while on vacation or business trips |
| Multi-Location | Access printers at different sites through one Bambuddy |
| Team Workshop | Let team members print without local network access |
Proxy Mode vs Other Modes¶
| Feature | Archive | Review | Queue | Proxy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Files stored locally | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Sends to real printer | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Remote printing | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Requires target printer | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Uses printer's access code | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
Proxy Mode Troubleshooting¶
Slicer can't connect:
- Verify port forwarding is configured correctly
- Check that Bambuddy's proxy is running (green status indicator)
- Ensure your firewall allows incoming connections on ports 990, 8883, and 50000-50100
Authentication fails:
- Use your printer's access code, not a Bambuddy password
- The access code is the same one you'd use for LAN mode printing
Connection drops during transfer:
- Large files may timeout on slow connections
- Check your internet upload speed
Printer shows offline in slicer:
- Verify the target printer is online in Bambuddy
- Check that the printer is in LAN mode
- Restart the proxy by toggling it off and on
 Setup Required¶
Setup Required¶
Important: Read Before Enabling
The virtual printer feature requires additional system configuration before it will work. Simply enabling it in the UI is not enough!
The virtual printer uses privileged port 990 (FTPS) which requires special handling on most systems.
Required Ports¶
| Service | Port | Protocol | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| SSDP | 2021 | UDP | Printer discovery (same LAN only) |
| MQTT | 8883 | TCP/TLS | Printer communication |
| FTPS | 990 | TCP/TLS | File transfer control |
| FTP Data | 50000-50100 | TCP | File transfer data |
Certificate Installation¶
Required Step
The virtual printer uses TLS encryption with a self-signed CA certificate. Bambu Studio and OrcaSlicer do not use the system certificate store - you must add the certificate directly to the slicer's certificate file.
Step 1: Locate the CA Certificate¶
The Bambuddy CA certificate is at:
- Native install:
data/virtual_printer/certs/bbl_ca.crt - Docker: Extract with
docker cp bambuddy:/app/data/virtual_printer/certs/bbl_ca.crt ./bambuddy-ca.crt
Certificate Generation
The certificate is only generated when you first enable the virtual printer in the UI. If the file doesn't exist, enable the virtual printer first.
Step 2: Append the Bambuddy CA Certificate to Slicer¶
The slicer's printer.cer file contains PEM certificates. You need to append the Bambuddy CA certificate to this file.
Open printer.cer in a text editor and:
- Go to the end of the file
- Paste the entire contents of
bambuddy-ca.crtafter the last-----END CERTIFICATE----- - Save the file
- Fully restart the slicer (Cmd+Q on macOS, not just close the window)
Keep Original Certificates
Appending (rather than replacing) preserves your ability to connect to physical Bambu Lab printers while also enabling the virtual printer.
Certificate file locations:
- Bambu Studio:
/Applications/BambuStudio.app/Contents/Resources/cert/printer.cer - OrcaSlicer:
/Applications/OrcaSlicer.app/Contents/Resources/cert/printer.cer
- Bambu Studio:
C:\Program Files\Bambu Studio\resources\cert\printer.cer - OrcaSlicer:
C:\Program Files\OrcaSlicer\resources\cert\printer.cer
- Bambu Studio:
~/.local/share/BambuStudio/resources/cert/printer.cer - OrcaSlicer:
~/.local/share/OrcaSlicer/resources/cert/printer.cer
When to Update the Certificate
You must update the printer.cer file whenever:
- First-time setup - append the Bambuddy CA certificate
- New Bambuddy installation - each install generates a unique CA
- Switching Bambuddy hosts - each host has its own CA (unless you share the CA)
- After slicer updates - updates may restore the original certificate file, requiring you to append again
Certificate Persistence¶
The CA certificate is generated once and persists across Bambuddy restarts. If you switch between Docker and native installations, share the certificate directory to avoid regenerating:
Multiple Bambuddy Hosts¶
Each Bambuddy installation generates its own unique CA certificate.
One Bambuddy CA at a Time
When switching between Bambuddy hosts with different CAs, remove the old Bambuddy CA and append the new one. Having multiple Bambuddy CAs may cause confusion about which host to connect to.
Option 1: Share the CA (Recommended)
Copy the certs/ directory from one host to all others:
# Copy certs from host1 to host2
scp -r host1:/path/to/data/virtual_printer/certs/ host2:/path/to/data/virtual_printer/
Then restart Bambuddy on host2. All hosts will use the same CA, so one certificate in the slicer works for all.
Option 2: Update Certificate When Switching Hosts
Each time you switch to a different Bambuddy host:
- Extract the CA from the new host
- Open the slicer's
printer.cerfile - Remove the old Bambuddy CA (if present) and append the new one
- Fully restart the slicer
Platform Setup¶
Choose your platform below for specific setup instructions.
Linux (Native Installation)¶
Port 990 is a privileged port. You need iptables rules to redirect it:
# Redirect incoming traffic on port 990 to 9990
sudo iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 990 -j REDIRECT --to-port 9990
# Redirect localhost traffic on port 990 to 9990
sudo iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -o lo -p tcp --dport 990 -j REDIRECT --to-port 9990
Make rules persistent:
Firewall rules (if using UFW):
sudo ufw allow 2021/udp # SSDP
sudo ufw allow 8883/tcp # MQTT
sudo ufw allow 990/tcp # FTPS
sudo ufw allow 9990/tcp # FTPS internal
sudo ufw allow 50000:50100/tcp # FTP passive data
Firewall rules (if using firewalld):
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=2021/udp # SSDP
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=8883/tcp # MQTT
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=990/tcp # FTPS
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=9990/tcp # FTPS internal
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=50000-50100/tcp # FTP passive data
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Docker (Linux)¶
Docker requires host networking for SSDP discovery to work.
docker-compose.yml:
services:
bambuddy:
image: ghcr.io/maziggy/bambuddy:latest
container_name: bambuddy
network_mode: host # Required for SSDP discovery
volumes:
- bambuddy_data:/app/data
- bambuddy_logs:/app/logs
environment:
- TZ=Europe/Berlin
restart: unless-stopped
volumes:
bambuddy_data:
bambuddy_logs:
You still need iptables rules on the host:
sudo iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 990 -j REDIRECT --to-port 9990
sudo iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -o lo -p tcp --dport 990 -j REDIRECT --to-port 9990
Make rules persistent (Debian/Ubuntu):
Firewall rules (if using UFW):
sudo ufw allow 2021/udp # SSDP
sudo ufw allow 8883/tcp # MQTT
sudo ufw allow 990/tcp # FTPS
sudo ufw allow 9990/tcp # FTPS internal
sudo ufw allow 50000:50100/tcp # FTP passive data
Firewall rules (if using firewalld):
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=2021/udp # SSDP
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=8883/tcp # MQTT
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=990/tcp # FTPS
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=9990/tcp # FTPS internal
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=50000-50100/tcp # FTP passive data
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Docker (macOS / Windows)¶
Limited Support
Docker Desktop on macOS and Windows doesn't support host network mode. SSDP discovery will not work - you must add the printer manually by IP.
- Use bridge networking with port mapping
- Add the printer manually in your slicer using the host IP address
- Virtual printer discovery from slicers won't work
Unraid¶
-
Set Network Type to
hostin container settings -
Add iptables rules via Unraid terminal:
-
Make rules persistent by adding to
/boot/config/go:
Synology NAS¶
-
Use Host Network in Container Manager
-
SSH into your NAS and add iptables rules:
-
Create a scheduled task to restore rules on boot:
- Control Panel → Task Scheduler → Create → Triggered Task → User-defined script
- Event: Boot-up
- Script:
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 990 -j REDIRECT --to-port 9990
TrueNAS SCALE¶
-
Use Host Network when creating the app/container
-
Add iptables rules via shell:
Proxmox LXC¶
-
Enable nesting in container options (for iptables support)
-
Inside the LXC:
Configuration¶
Enabling the Virtual Printer¶
- Complete the platform setup above first
- Go to Settings in Bambuddy
- Scroll to the Virtual Printer section
- Set an Access Code (exactly 8 characters)
- Toggle Enable Virtual Printer to on
- Choose your Archive Mode:
- Immediate: Files are archived automatically when received
- Queue for Review: Files go to pending uploads for manual review
Printer Model Selection¶
Choose which Bambu printer model the virtual printer should emulate:
| SSDP Code | Printer | Serial Prefix |
|---|---|---|
| 3DPrinter-X1-Carbon | X1C | 00M |
| 3DPrinter-X1 | X1 | 00M |
| C13 | X1E | 03W |
| C11 | P1P | 01S |
| C12 | P1S | 01P |
| N7 | P2S | 22E |
| N2S | A1 | 039 |
| N1 | A1 Mini | 030 |
| O1D | H2D | 094 |
| O1S | H2S | 094 |
Model Change
Changing the printer model will automatically restart the virtual printer. You may need to refresh the device list in your slicer.
Adding to Bambu Studio / Orca Slicer¶
When Does Automatic Discovery Work?
SSDP discovery only works when the slicer and Bambuddy are on the same network segment (same LAN/subnet). You must add the printer manually by IP when:
- Connecting over a VPN (WireGuard, Tailscale, etc.)
- Using Docker bridge mode (macOS/Windows)
- Connecting over the internet via port forwarding
- The slicer is on a different subnet than Bambuddy
Automatic Discovery¶
- Ensure the virtual printer is enabled and running
- In Bambu Studio/Orca Slicer, go to Device tab
- Click Refresh or wait for discovery
- The virtual printer "Bambuddy" should appear
- Click to add it, entering the access code when prompted
Manual Addition¶
If automatic discovery doesn't work:
- In Bambu Studio, go to Device → Add Printer
- Select Add printer by IP
- Enter the IP address of your Bambuddy server
- Enter the access code
- The printer will be added to your device list
Sending Prints to Bambuddy¶
Use Send, Not Print
You must use the Send button, not the Print button!
- Send → Transfers the file to Bambuddy (correct)
- Print → Attempts to start printing immediately (won't work)
How to Send a Print¶
- Slice your model as usual
- Select "Bambuddy" (or your virtual printer name) from the printer dropdown
- Click the Send button (next to the Print button)
- The file will be transferred to Bambuddy
What Happens Next¶
Depending on your Archive Mode setting:
- Immediate: The file is automatically archived
- Queue for Review: The file appears in Pending Uploads for you to review, assign to a project, add notes, or queue for printing
Send Button Location
In Bambu Studio/OrcaSlicer, the Send button is typically a small icon next to the large Print button, or accessible via the dropdown arrow on the Print button.
Troubleshooting¶
Printer Not Appearing in Slicer¶
- Check virtual printer is enabled and showing "Running" status
- Verify iptables rules are active:
- Check firewall - ports 2021/udp, 8883/tcp, 990/tcp, 50000-50100/tcp must be open
- Same network - slicer and Bambuddy must be on the same subnet
FTP Error / Connection Reset¶
- Verify iptables rules are correctly configured
- Check permissions on the uploads directory
- Check no other FTP server is using port 990
- Review logs for specific error messages
"Wrong Printer Model" Error¶
The slicer's selected printer profile must match the virtual printer model in Bambuddy settings.
Permission Denied Errors¶
If you see "Permission denied" in the logs:
# Fix ownership of the virtual printer directory
sudo chown -R $(whoami):$(whoami) /path/to/bambuddy/data/virtual_printer
Authentication Failed¶
- Verify access code matches in both Bambuddy and slicer
- Access code must be exactly 8 characters
- Try removing and re-adding the printer in your slicer
Wrong IP in SSDP / TLS Handshake Fails (Multi-NIC)¶
If Bambuddy has multiple network interfaces (LAN + VPN, Docker bridges, etc.), the auto-detected IP may be on the wrong interface:
- Go to Settings → Virtual Printer
- Enable the virtual printer if not already enabled
- Under Network Interface Override, select the interface your slicer connects through
- The virtual printer will restart with the correct IP in SSDP broadcasts and TLS certificate
TLS Connection Failed / Error -1¶
This typically means the slicer doesn't trust the virtual printer's certificate:
-
Verify Bambuddy CA is in slicer's certificate file:
-
Wrong certificate? If you have multiple Bambuddy hosts or reinstalled, you must update the certificate. See Step 2.
-
Verify certificate fingerprints match:
Verify this fingerprint appears in one of the certificates in your slicer's# On Bambuddy server (Docker) docker exec bambuddy openssl x509 -in /app/data/virtual_printer/certs/bbl_ca.crt -noout -fingerprint -sha1 # On Bambuddy server (native) openssl x509 -in data/virtual_printer/certs/bbl_ca.crt -noout -fingerprint -sha1printer.cer. -
Fully restart the slicer - Cmd+Q on macOS, or End Task on Windows. Just closing the window is not enough.
-
Regenerate certificates (last resort):
You'll need to remove the old Bambuddy CA from the slicer and append the new one.
Technical Details¶
Security¶
- MQTT control channel: Fully TLS-encrypted (slicer <-> Bambuddy <-> printer)
- FTP control channel: Fully TLS-encrypted (slicer <-> Bambuddy <-> printer)
- FTP data channel: Encrypted between Bambuddy and printer. Not encrypted between slicer and Bambuddy due to a Bambu Studio limitation. Use a VPN for end-to-end data encryption.
- Self-signed certificates are auto-generated
- Access code authentication required for all connections
- Certificates stored in
data/virtual_printer/certs/
Limitations¶
- Only one virtual printer instance per Bambuddy installation
- SSDP discovery requires same LAN — use manual IP entry for VPN, remote, or Docker bridge setups
- Slicer must trust the self-signed certificate
- FTP data channel unencrypted on slicer side (use VPN for full encryption)